BoC set to keep rates unchanged, stressing a data-dependent approach
- The Bank of Canada is expected to keep its interest rate at 2.25%.
- The Canadian Dollar remains firm, dragging USD/CAD to yearly lows.
- Markets pencil in around 10 bps of hiking by the BoC this year.
The Bank of Canada (BoC) is widely expected to leave its benchmark rate unchanged at 2.25% at Wednesday’s meeting, extending the pause it signalled back in December.
At its last decision, the central bank made clear it sees policy as roughly where it needs to be to keep inflation close to the 2% target, so long as the economy behaves as expected. Still, officials were keen to underline that they’re not locked in and stand ready to respond if the outlook deteriorates or inflation risks re-emerge.
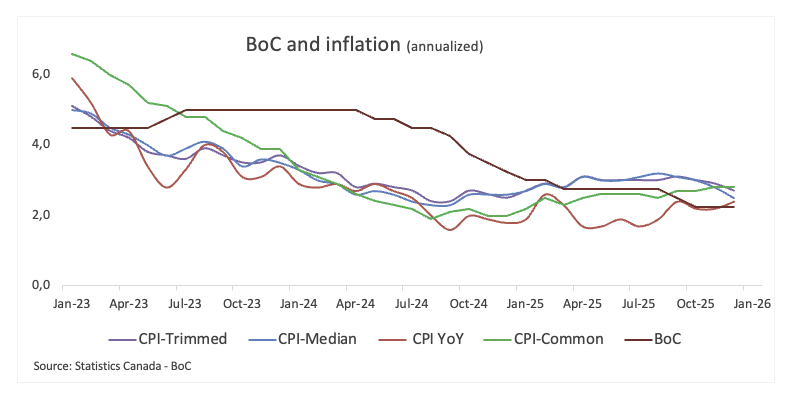
On inflation, the message remains cautiously reassuring. Headline CPI is projected to hover near the target as spare capacity in the economy helps offset cost pressures tied to trade reconfiguration. Even so, underlying inflation is still running a little hot, suggesting the disinflation process isn’t complete.
The growth picture is also uneven: Q4 GDP is expected to come in soft, with firmer domestic demand likely to be outweighed by a drag from net exports. That follows a surprisingly strong Q3, which the BoC has largely put down to trade-related volatility rather than a genuine pickup in momentum. The labour market offers a slightly brighter note, with early signs of improvement reinforcing the Bank’s wait-and-see approach.
Inflation, however, remains the key watchpoint after the headline CPI edged up to 2.4% YoY in December, while core inflation eased to 2.8% YoY. The bank’s preferred measures, CPI-Common, Trimmed and Median, also ticked lower, but at 2.8%, 2.7% and 2.5% respectively, they remain comfortably above target.
Previewing the BoC’s interest rate decision, analysts at the National Bank of Canada (NBC) noted, “The Bank of Canada is set to leave its overnight target unchanged at 2.25%, a decision widely expected by forecasters and OIS markets. This would mark the second consecutive hold after policymakers declared in October that policy is at ‘about the right level’ to keep inflation near target and support the economy’s transition”.
When will the BoC release its monetary policy decision, and how could it affect USD/CAD?
The Bank of Canada will announce its policy decision on Wednesday at 14:45 GMT alongside the Monetary Policy Report (MPR), followed by a press conference with Governor Tiff Macklem at 15:30 GMT.
Markets anticipate the central bank will maintain its current stance, with a projected tightening of approximately 10 basis points by the end of 2026.
Pablo Piovano, Senior Analyst at FXStreet, points out that the CAD has been appreciating steadily against the Greenback since its yearly lows past the 1.3900 barrier recorded earlier in the month. He adds: “Indeed, USD/CAD has recently broken below the 1.3700 support to hit new 2026 lows, exposing a potential test of the December 2025 floor at 1.3642 (December 26). South from here sits the weekly trought at 1.3575 (July 23), ahead of the July 2025 base at 1.3556 (July 3) and the 2025 bottom at 1.3538 (June 16).”
From here, Piovano says a return of bullish momentum could prompt USD/CAD to initially reclaim its key 200-day SMA at 1.3833 prior to the 2026 ceiling at 1.3928 (January 16). Up from here comes the key 1.4000 threshold seconded by the November top at 1.4140 (November 5).
“Momentum favours extra declines,” he adds, noting that the Relative Strength Index (RSI) approaches the 33 level and the Average Directional Index (ADX) near 27 is indicative of a pretty firm trend.
Canadian Dollar FAQs
The key factors driving the Canadian Dollar (CAD) are the level of interest rates set by the Bank of Canada (BoC), the price of Oil, Canada’s largest export, the health of its economy, inflation and the Trade Balance, which is the difference between the value of Canada’s exports versus its imports. Other factors include market sentiment – whether investors are taking on more risky assets (risk-on) or seeking safe-havens (risk-off) – with risk-on being CAD-positive. As its largest trading partner, the health of the US economy is also a key factor influencing the Canadian Dollar.
The Bank of Canada (BoC) has a significant influence on the Canadian Dollar by setting the level of interest rates that banks can lend to one another. This influences the level of interest rates for everyone. The main goal of the BoC is to maintain inflation at 1-3% by adjusting interest rates up or down. Relatively higher interest rates tend to be positive for the CAD. The Bank of Canada can also use quantitative easing and tightening to influence credit conditions, with the former CAD-negative and the latter CAD-positive.
The price of Oil is a key factor impacting the value of the Canadian Dollar. Petroleum is Canada’s biggest export, so Oil price tends to have an immediate impact on the CAD value. Generally, if Oil price rises CAD also goes up, as aggregate demand for the currency increases. The opposite is the case if the price of Oil falls. Higher Oil prices also tend to result in a greater likelihood of a positive Trade Balance, which is also supportive of the CAD.
While inflation had always traditionally been thought of as a negative factor for a currency since it lowers the value of money, the opposite has actually been the case in modern times with the relaxation of cross-border capital controls. Higher inflation tends to lead central banks to put up interest rates which attracts more capital inflows from global investors seeking a lucrative place to keep their money. This increases demand for the local currency, which in Canada’s case is the Canadian Dollar.
Macroeconomic data releases gauge the health of the economy and can have an impact on the Canadian Dollar. Indicators such as GDP, Manufacturing and Services PMIs, employment, and consumer sentiment surveys can all influence the direction of the CAD. A strong economy is good for the Canadian Dollar. Not only does it attract more foreign investment but it may encourage the Bank of Canada to put up interest rates, leading to a stronger currency. If economic data is weak, however, the CAD is likely to fall.
Tariffs FAQs
Tariffs are customs duties levied on certain merchandise imports or a category of products. Tariffs are designed to help local producers and manufacturers be more competitive in the market by providing a price advantage over similar goods that can be imported. Tariffs are widely used as tools of protectionism, along with trade barriers and import quotas.
Although tariffs and taxes both generate government revenue to fund public goods and services, they have several distinctions. Tariffs are prepaid at the port of entry, while taxes are paid at the time of purchase. Taxes are imposed on individual taxpayers and businesses, while tariffs are paid by importers.
There are two schools of thought among economists regarding the usage of tariffs. While some argue that tariffs are necessary to protect domestic industries and address trade imbalances, others see them as a harmful tool that could potentially drive prices higher over the long term and lead to a damaging trade war by encouraging tit-for-tat tariffs.
During the run-up to the presidential election in November 2024, Donald Trump made it clear that he intends to use tariffs to support the US economy and American producers. In 2024, Mexico, China and Canada accounted for 42% of total US imports. In this period, Mexico stood out as the top exporter with $466.6 billion, according to the US Census Bureau. Hence, Trump wants to focus on these three nations when imposing tariffs. He also plans to use the revenue generated through tariffs to lower personal income taxes.